Difference between revisions of "Series Material"
From OpenSeesWiki
Jump to navigationJump to search| (2 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 4: | Line 4: | ||
{| | {| | ||
| − | | style="background: | + | | style="background:lime; color:black; width:800px" | '''uniaxialMaterial Series $matTag $tag1 $tag2 ...''' |
|} | |} | ||
| Line 15: | Line 15: | ||
|} | |} | ||
| − | The | + | The series material is represented graphically: |
[[Image:SeriesMaterial.gif]] | [[Image:SeriesMaterial.gif]] | ||
| − | In a | + | In a series model, stresses are equal and strains and flexibilities are additive: |
[[Image:SeriesMaterialExample.gif]] | [[Image:SeriesMaterialExample.gif]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | NOTE: | ||
| + | |||
| + | - The series material ignores strain rate effects of its component materials | ||
---- | ---- | ||
Latest revision as of 19:39, 7 July 2023
This command is used to construct a series material object made up of an arbitrary number of previously-constructed UniaxialMaterial objects.
| uniaxialMaterial Series $matTag $tag1 $tag2 ... |
| $matTag | integer tag identifying material |
| $tag1 $tag2 ... | identification tags of materials making up the material model |
The series material is represented graphically:
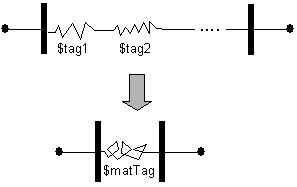
In a series model, stresses are equal and strains and flexibilities are additive:
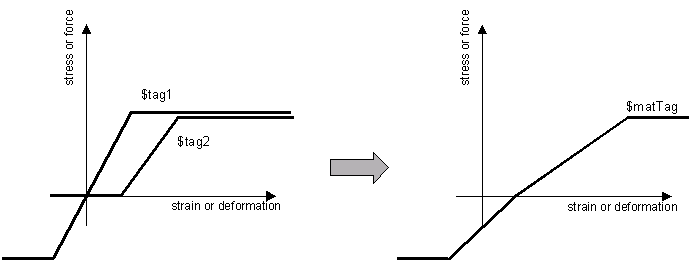
NOTE:
- The series material ignores strain rate effects of its component materials
Code Developed by: Micheal Scott, Oregon State University
Images Developed by: Silvia Mazzoni