|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Objectives and Characteristics
|
Model Types
|
Analysis Types
|
Example 3. Cantilever Column with units
|
|
|
|
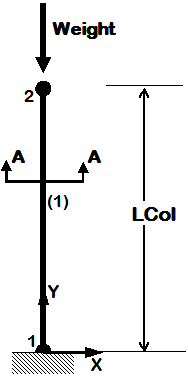
|
- units, defined and used (they will be used in all subsequent examples)
- separate model-building and analysis files
|
- elastic elements
- inelastic uniaxial section
- fiber section (Reinforced-concrete fiber section)
|
- static pushover analysis
- dynamic earthquake-input analysis (uniform excitation)
|
Example 4. Portal Frame
|
|
|
|
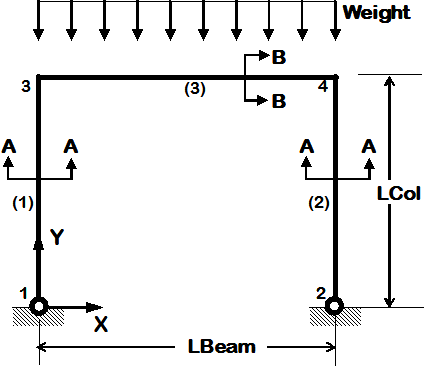
|
- use previously-defined procedures to simplify input
- source Tcl script segments (series of commonly-used input commands)
- introduce more analysis types
- introduce procedure to read database input motion files (data with text in first lines)
|
- elastic elements
- inelastic uniaxial section
- inelastic fiber section (Reinforced-concrete fiber section)
|
- static pushover analysis
- static reversed cyclic analysis
- dynamic sine-wave input analysis (uniform excitation)
- dynamic earthquake-input analysis (uniform excitation)
- dynamic sine-wave input analysis (multiple-support excitation)
- dynamic earthquake-input analysis (multiple-support excitation)
- dynamic bidirectional earthquake-input analysis (uniform excitation)
|
Example 5. 2D Frame, 3-story, 3-bay
|
|
|
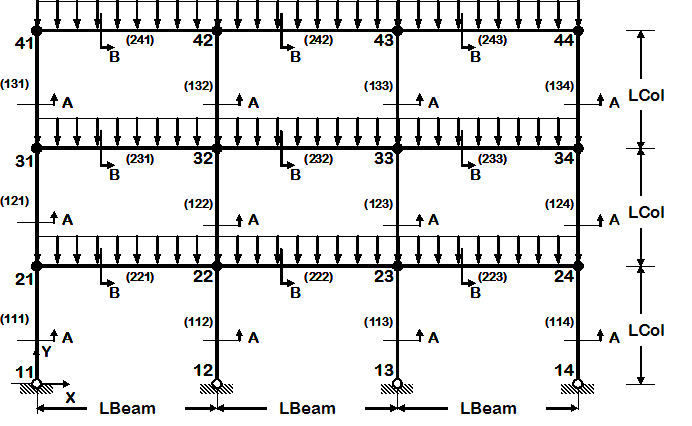
|
- 2D frame of fixed geometry: 3-story, 3-bay
- nodes and elements are defined manually, one by one
- move script library files and ground-motion into their own directory (so they can be used by other examples)
- introduce some W-section procedures
|
- Steel W Section
- elastic uniaxial section
- inelastic uniaxial section
- inelastic fiber section
|
- static pushover analysis
- static reversed cyclic analysis
- dynamic sine-wave input analysis (uniform excitation)
- dynamic earthquake-input analysis (uniform excitation)
- dynamic sine-wave input analysis (multiple-support excitation)
- dynamic earthquake-input analysis (multiple-support excitation)
- dynamic bidirectional earthquake-input analysis (uniform excitation)
|
Example 6. generic 2D Frame, N-story, N-bay
|
|
|
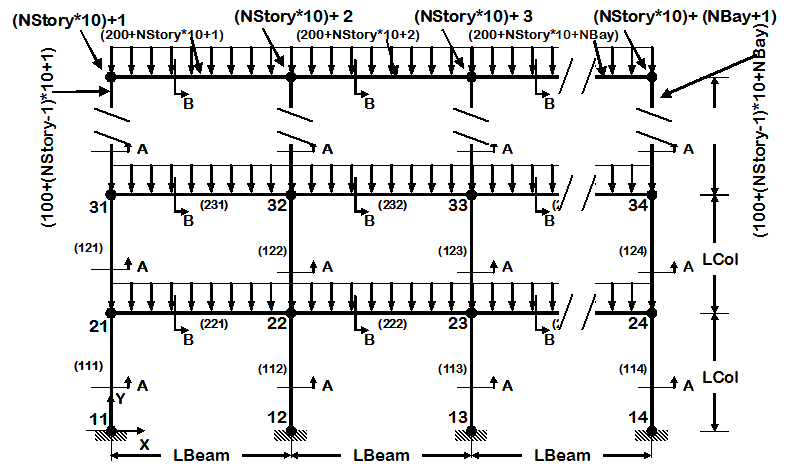
|
- 2D frame geometry of variable geometry ( # stories and # bays are variables)
- node and element definition is automated
- use previously-defined procedures to view model node numbers and elements, deformed shape, and displacement history, in 2D
|
- Steel W Section
- elastic uniaxial section
- inelastic uniaxial section
- inelastic fiber section
|
- static pushover analysis
- static reversed cyclic analysis
- dynamic sine-wave input analysis (uniform excitation)
- dynamic earthquake-input analysis (uniform excitation)
- dynamic sine-wave input analysis (multiple-support excitation)
- dynamic earthquake-input analysis (multiple-support excitation)
- dynamic bidirectional earthquake-input analysis (uniform excitation)
|