This is a great example!
To all the demonstrations that Example 3 has done, Example 4 adds the use of previously-defined Tcl procedures (procs) or scripts.
This example also introduces new kinds of static and dynamic analyses.
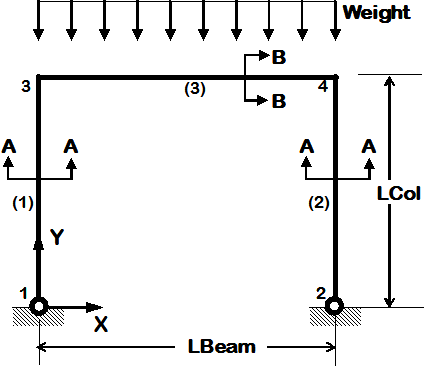
Procedures define a series of commands on specified arguments. They have a series of input variables and are executed like new commands. Tcl scripts do not take arguments. Both consist of generalized series of commands that are used more than once within a single input file, or are transferrable to other input files. The following library files include tasks that are achieved by Tcl procs or script segments and are used in this example:
Model Building |
|
define units and constants |
|
Static Lateral-Load Analysis |
|
define displacement increments for reversed cyclic displacement paths |
|
define static-analysis parameters for lateral-load analysis |
|
Dynamic Lateral-Load Analysis |
|
define dynamic-analysis parameters for lateral-load analysis |
|
define a procedure which parses a ground motion record from the PEER strong motion database by finding dt in the record header, then echoing data values to the output file. |
|
The following types of analyses are included in this example:
Static Analysis |
|
static pushover analysis |
lateral loads are applied to the structure until a maximum specified displacement is reached |
static reversed cyclic analysis |
lateral loads are applied (and reversed) to the structure to achieve a specified series of reversed displacement cycles of increasing magnitude |
Dynamic Analysis |
|
dynamic sine-wave input analysis (uniform excitation) |
a ground acceleration in sine-wave form is applied uniformly to all supports |
dynamic earthquake-input analysis (uniform excitation) |
a ground acceleration in recorded-earthquake form is applied uniformly to all supports
|
dynamic sine-wave input analysis (multiple-support excitation) |
a ground displacement in sine-wave form is applied the supports. different inputs can be specified for different nodes |
dynamic earthquake-input analysis (multiple-support excitation) |
a ground displacement in recorded-earthquake form is applied the supports. different inputs can be specified for different nodes |