Structural Models
The examples included in this chapter provide a library of structural models. These examples take advantage of the Tcl scripting language starting from simple variable substitutions in the initial examples, to the more advanced techniques of array management and logical expressions (if-then statements).
As the example number increases, so does its sophistication. The user is recommended to follow the numerical order of the examples as the starter point.
There are three sets of input files for these examples:
1. Model-Building --
- define units
- define the geometry of the model, such as nodal coordinates, nodal constraints, section properties and element connectivity, and recorders (for output)
- define nodal masses
- define and apply gravity loads
2. Static Lateral-Load Analysis:
- define the lateral-load pattern for the static loads
- define the displacement increments and displacement path
- define all parameters for static analysis
- perform the analysis
3. Dynamic Lateral-Load Analysis
- define the input motion and all associated parameters, such as scaling and input type
- define all parameters for transient (dynamic) analysis
- define analysis duration and time increment
- perform dynamic analysis
Each part has a number of different options:
|
|
|
|
|
|
Models
|
|
|
Elastic Elements
- axial and flexural stiffnesses are defined at element level
|
E, I, A
|
|
Distributed Plasticity
|
|
|
|
Uniaxial Section
- Axial and flexural stiffnesses/strength are defined independently at the section level
|
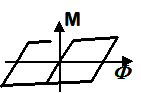
|
|
Fiber Section
- The section is broken down into fibers where uniaxial materials are defined independently. The program calculates flexural and axial stiffnesses/strength by integrating strains across the section.
|
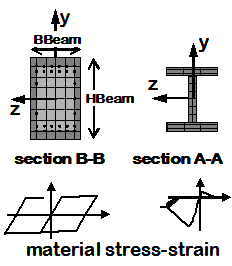
|
|
Analyses
|
|
|
Static Analyses
|
|
|
Pushover
- One-directional displacement-controlled static loading
|
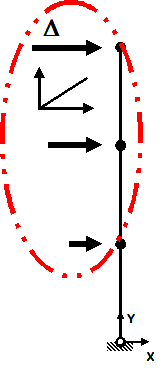
|
|
|
Reversed Cyclic
- One-directional displacement-controlled static loading
- Displacement cycles are imposed in positive and negative direction
|
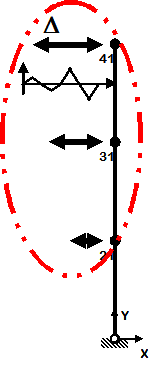
|
|
Dynamic Analyses
|
|
|
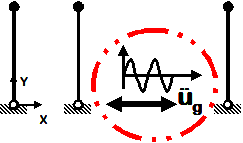
Uniform Sine-Wave
- Sine-wave acceleration input
- Same acceleration input at all nodes restrained in specified direction
|
|
|
|
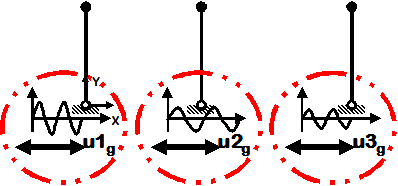
Multiple-Support Sine-Wave
- Sine-wave displacement input
- Different displacements are specified at particular nodes in specified directions
|
|
|
|
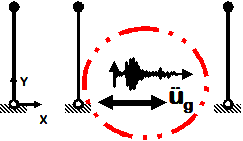
Uniform Earthquake
- Earthquake (from file) acceleration input
- Same acceleration input at all nodes restrained in specified direction
|
|
|
|
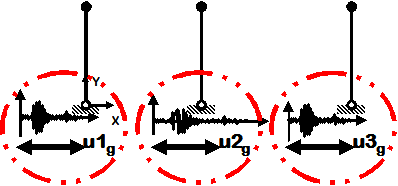
Multiple-Support Earthquake
- Earthquake (from file) displacement input
- Different displacements are specified at particular nodes in specified directions
|
|
|
|
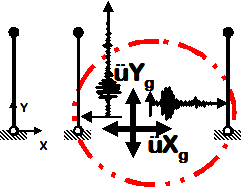
Bidirectional Earthquake
- Earthquake (from file) acceleration input
- Different inputs are specified for two directions
- Same acceleration input at all nodes restrained in specified directions
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Each example also has a set of Tcl Script Libraries. They are, however, called by the input files themselves, not by direct user commands. These library files define generalized procedures that are model independent. Different examples may use the same Tcl Script Library files. For example, LibDisplay.tcl contains a number of procedures for viewing the model. These procedures can be used on any model.