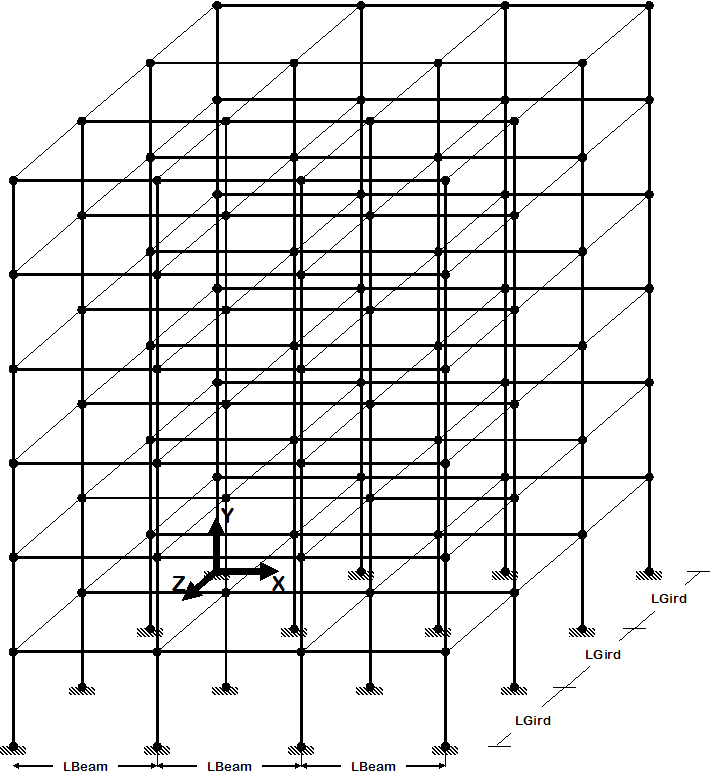
Just like Example 6 for the 2D frame, this example utilizes Tcl variable-substitution and array-management tools to optimize the building of the numerical model of a generic 3D frame. The user is prompted for the number of stories and the number of bays (the can also be fixed in the input file).
The same items for 3D modelling as the frame shown in Example 7 are considered here.
For this example, there is one model-building file with many options for the model. In addition to specific dynamic-analysis files, there is also a dynamic-analysis file where the user is given the option of which dynamic analysis to perform.
The following library files include tasks that are achieved by Tcl procs or script segments and are used in this example:
Model Building |
|
define units and constants |
|
define displacement increments for reversed cyclic displacement paths |
|
define procedures for creating standard W-section fiber sections and get section properties |
|
define materials for reinforced-concrete section |
|
define procedures for creating reinforced-concrete fiber sections |
|
procedure for displaying a plane in model |
|
procedure for displaying 3D perspectives of model |
|
Static Lateral-Load Analysis |
|
define static-analysis parameters for lateral-load analysis |
|
Dynamic Lateral-Load Analysis |
|
define dynamic-analysis parameters for lateral-load analysis |
|
define a procedure which parses a ground motion record from the PEER strong motion database by finding dt in the record header, then echoing data values to the output file. |
|
The following figure shows the frame layout: