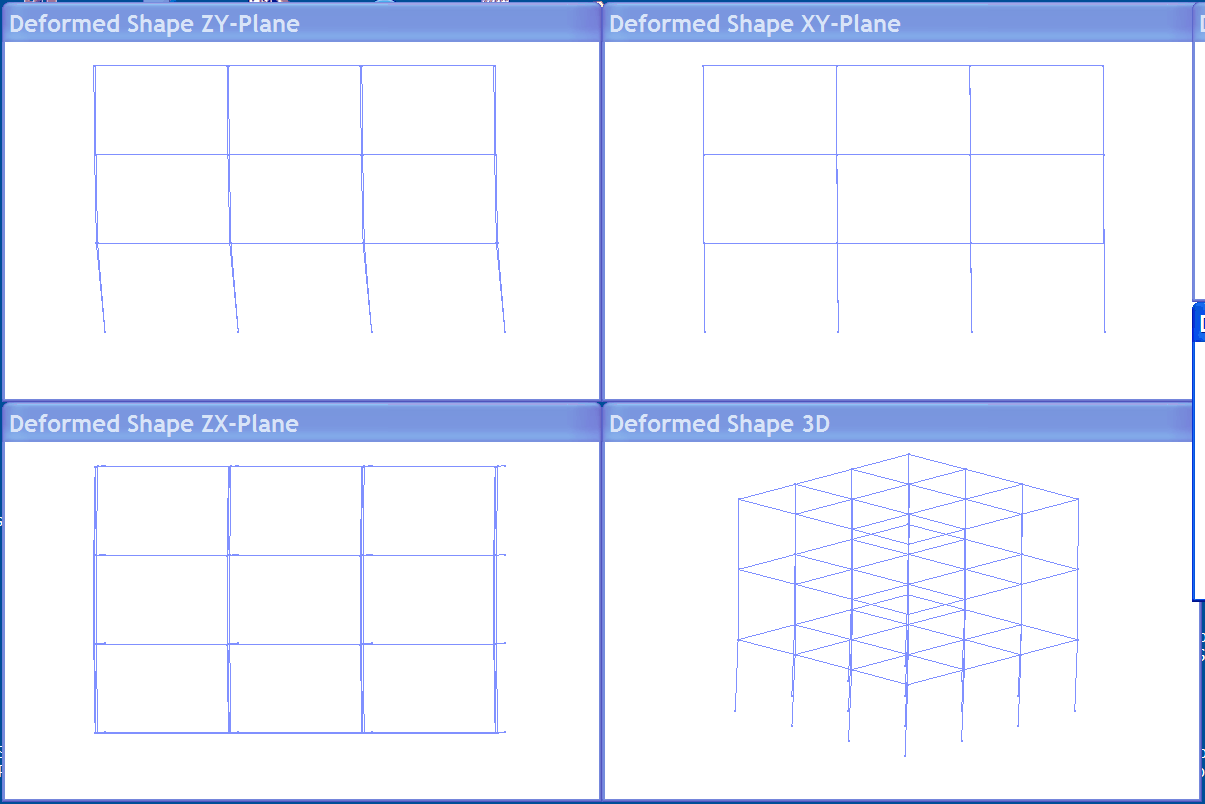
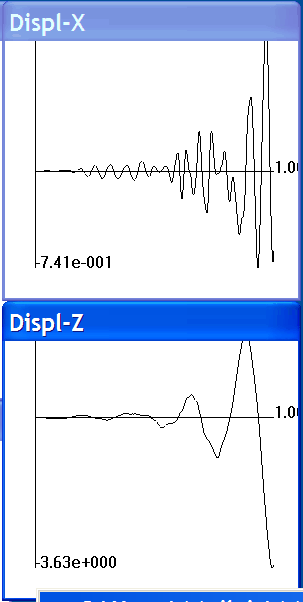
|
|
|
- Define & apply lateral load
- Similar to Example 7, vector operations are used to determine load distributions
|
|
Dynamic Uniform Sine-Wave Ground Motion
- Sine-wave acceleration input
- Same acceleration input at all nodes restrained in specified direction
|
|
Dynamic Uniform Earthquake Ground Motion (typical)
- Earthquake (from file) acceleration input
- Same acceleration input at all nodes restrained in specified direction
|
|
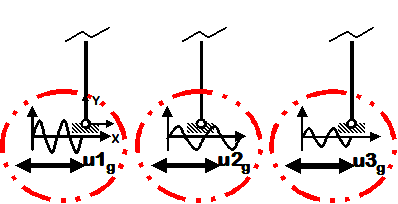
Dynamic Multiple-Support Sine-Wave Ground Motion
- Sine-wave displacement input
- Different displacements are specified at particular nodes in specified directions (all nodes in this example)
|
|
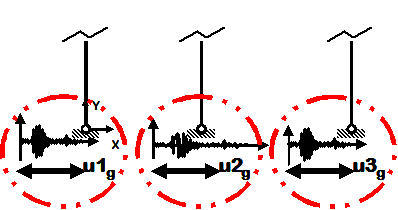
Dynamic Multiple-Support Earthquake Ground Motion
- Earthquake (from file) displacement input
- Different displacements are specified at particular nodes in specified directions
|
|
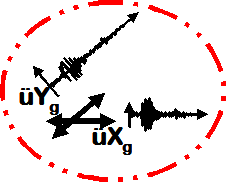
Bidirectional Dynamic Uniform Earthquake Ground Motion
- Earthquake (from file) acceleration input
- Different inputs are specified for two directions
- Same acceleration input at all nodes restrained in specified directions
|
|