If the present ID used for the result is not of size equal to the
number of Vertices in theGraph, it deletes the old and
constructs a new ID. Starts by iterating through the Vertices of the
graph setting the tmp variable of each to -1. The Vertices are
then numbered using a depth first sort of the Graph, with each
unmarked Vertex in the Graph at a distance d from starting Vertex
being placed in the d'th level set. As this is RCM, the Vertices in
level set n are assigned a higher number than those in level set
n+1 with the tmp variable of the starting Vertex being
assigned numVertices -1. The tags of the Vertices are
placed into the ID at location given by their tmp variable. These
are replaced with the ref variable of each Vertex, which is
returned on successful completion.
The Vertex chosen as the starting Vertex is the one whose tag is given
by lastVertex. If this is -1 or the Vertex corresponding to
lastVertex does not exist then another Vertex is chosen. If the
GPS flag in constructor is false the first Vertex from the
Graphs VertexIter is used; if true a RCM numbering using the
first Vertex from the VertexIter is performed and the Vertices in the
last level set are then used to create an ID lastVertices with
which number(theGraph, lastVertices) can be invoked to determine
the numbering.
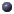 const ID& number(Graph &theGraph, const ID &lastVertices)
const ID& number(Graph &theGraph, const ID &lastVertices)
This method is invoked to determine the best starting Vertex for a RCM
using a Vertex whose tag is in lastVertices. To do a RCM
numbering is performed using each of the Vertices in
startVertices as the Vertex in level set 0. The Vertex which
results in the numbering with the smallest profile is chosen as
the starting Vertex. The RCM algorithm outlined above is then called
with this starting Vertex.
 int sendSelf(int commitTag, Channel &theChannel)
int sendSelf(int commitTag, Channel &theChannel)
Returns 0
 int recvSelf(int commitTag, Channel &theChannel, FEM_ObjectBroker &theBroker)
int recvSelf(int commitTag, Channel &theChannel, FEM_ObjectBroker &theBroker)
Returns 0



