Introduction
- Just like Example 6 for the 2D frame, this example utilizes Tcl variable-substitution and array-management tools to optimize the building of the numerical model of a generic 3D frame.
- The user is prompted for the number of stories and the number of bays (the can also be fixed in the input file).
- The same items for 3D modelling as the frame shown in Example 7 are considered here.
- For this example, there is one model-building file with many options for the model. In addition to specific dynamic-analysis files, there is also a dynamic-analysis file where the user is given the option of which dynamic analysis to perform.
Input
Model Building
- The following tasks are performed when building the model
- define units
- define model
- define recorders for output
- define & apply gravity
- The only difference between the two input files is in modelling the element section properties and calculating beam and column weight/mass.
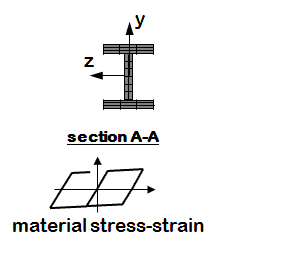
Steel W Section
Files
Notes
- 3D building frame: Steel W sections for both columns and beams. (variable elastic or fiber section)
- As of OpenSees version 3.2.2, you need to define torsion for the 3D fiber sections (https://wp.me/pbejzW-9X)
|
|
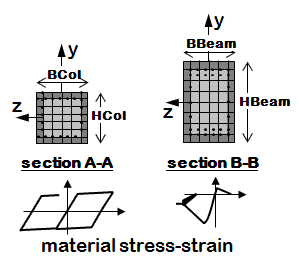
RC Section
Files
Notes
- 3D building frame: Reinforced-concrete rectangular sections for both columns and beams. (variable elastic or fiber section)
- As of OpenSees version 3.2.2, you need to define torsion for the 3D fiber sections (https://wp.me/pbejzW-9X)
|
|
Lateral-Load Analysis
The following tasks are performed in the analysis
- define lateral-load parameters
- analyze
Static
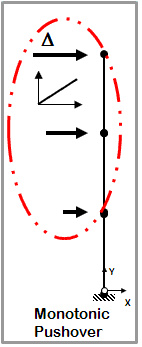
Static Pushover
Files
Notes
- One-directional monotonic displacement-controlled static loading
|
Static Reversed Cyclic

Files
Notes
- One-directional displacement-controlled static loading
- Displacement cycles are imposed in positive and negative direction
|
|
Dynamic EQ Ground Motion
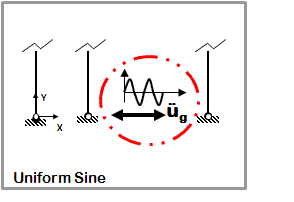
Dynamic Uniform Sine-Wave Ground Motion
Files
Notes
- Sine-wave acceleration input
- Same acceleration input at all nodes restrained in specified direction
|
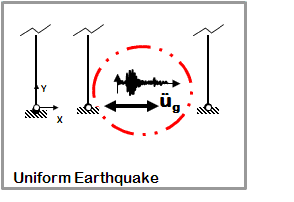
Dynamic Uniform Earthquake Ground Motion (typical)
Files
Notes
- Earthquake (from file) acceleration input
- Same acceleration input at all nodes restrained in specified direction
|
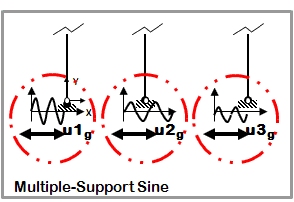
Dynamic Multiple-Support Sine-Wave Ground Motion
Files
Notes
- Sine-wave displacement input
- Different displacements are specified at particular nodes in specified directions
|
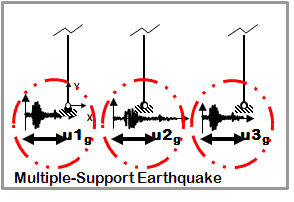
Dynamic Multiple-Support Earthquake Ground Motion
Files
Notes
- Earthquake (from file) displacement input
- Different displacements are specified at particular nodes in specified directions
|
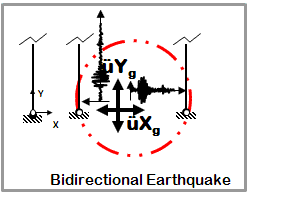
Dynamic Bidirectional Earthquake Ground Motion (typical)
Files
Notes
- Earthquake (from file) acceleration input
- Different ground motion in two directions
- Same acceleration input at all nodes restrained in specified direction
|
|
Run
The model and analysis combinations for this example are numerous. The following are an small subset, for demonstration purposes:
- To run W-Section Model, Static Pushover Analysis:
puts " -------------Elastic Model -------------"
puts " -------------Static Pushover Analysis -------------"
source Ex8.genericFrame3D.build.Wsec.tcl
source Ex8.genericFrame3D.analyze.Static.Push.tcl
- To run RC Model, Uniform Earthquake Excitation
puts " -------------Uniaxial Inelastic Section, Nonlinear Model -------------"
puts " -------------Uniform Earthquake Excitation -------------"
source Ex8.genericFrame3D.build.RCsec.tcl
source Ex8.genericFrame3D.analyze.Dynamic.EQ.Uniform.tcl
Notes
In this example, the following items are variables:
- Number of stories in Y direction
- Number of bays in X direction
- Number of bays in Z direction
- Elastic/Fiber Section
- Display: none/node numbering/deformed shape/mode shape (can choose which mode) (variable display scaling factor for both the deformed shape and the mode shape, this scaling factor is dependent on the user choice)
Return to OpenSees Examples Manual -- Structural Models & Analyses
Return to OpenSees User








