The following uniaxialMaterial objects were compared: Steel01, Steel02, Steel03, ReinforcingSteel and Hysteretic. The properties of each steel material were selected to be representative of a realistic material and to all have similar backbone and hysteretic curves. The following are the input commands used for each material type:
Please note that a symmetric curve was chosen for the Hysteretic material. Also, Steel02 and Steel03 are expected to exhibit the same behavior (The difference between these two materials lies in the availability of the source code). While the main envelope curve is similar for these materials, the differences between these materials are many and need to be studied carefully.
The values givein in Table 1 were chosen for the baseline in this study. Variations of Steel02, ReinforcingSteel and Hysteretic materials were further investigated, and presented in the subsequent sections. Because the different materials have different control arguments, these variations were studied within a material type and were not compared to other material types.
Table 1. Baseline Steel Material Properties (+Tension, -Compression).
Fy |
66.8ksi |
Yield Stress |
Es |
29000ksi |
Elastic Modulus |
epsY |
Fy/Es |
Yield Strain |
epsSH |
8*EpsY |
strain at onset of strain hardening |
Esh |
0.02*Es |
tangent stiffness at onset of strain hardening |
Bs |
0.01 |
ratio of post-yield tangent stiffness to elastic modulus (Steel01, Steel02, Steel03) |
Fy1 |
1.5*Fy |
post-yield maximum stress |
epsY1 |
epsY+(Fy1-Fy)/(Bs*Es) |
strain at Fy1 |
Fu |
1.2*Fy |
ultimate stress |
epsU |
0.25 |
strain at Fu |
pinchX |
1. |
pinching parameter (Hysteretic) |
pinchY |
1. |
pinching parameter (Hysteretic) |
damage1 |
0. |
damage parameter (Hysteretic) |
damage2 |
0. |
damage parameter (Hysteretic) |
betaMUsteel |
0. |
degraded unloading stiffness for hysteretic material based on MU^(-beta) (Hysteretic) |
R0 |
18 |
control the transition from elastic to plastic branches (Steel02, Steel03) |
cR1 |
0.925 |
control the transition from elastic to plastic branches (Steel02, Steel03) |
cR2 |
0.15 |
control the transition from elastic to plastic branches (Steel02, Steel03) |
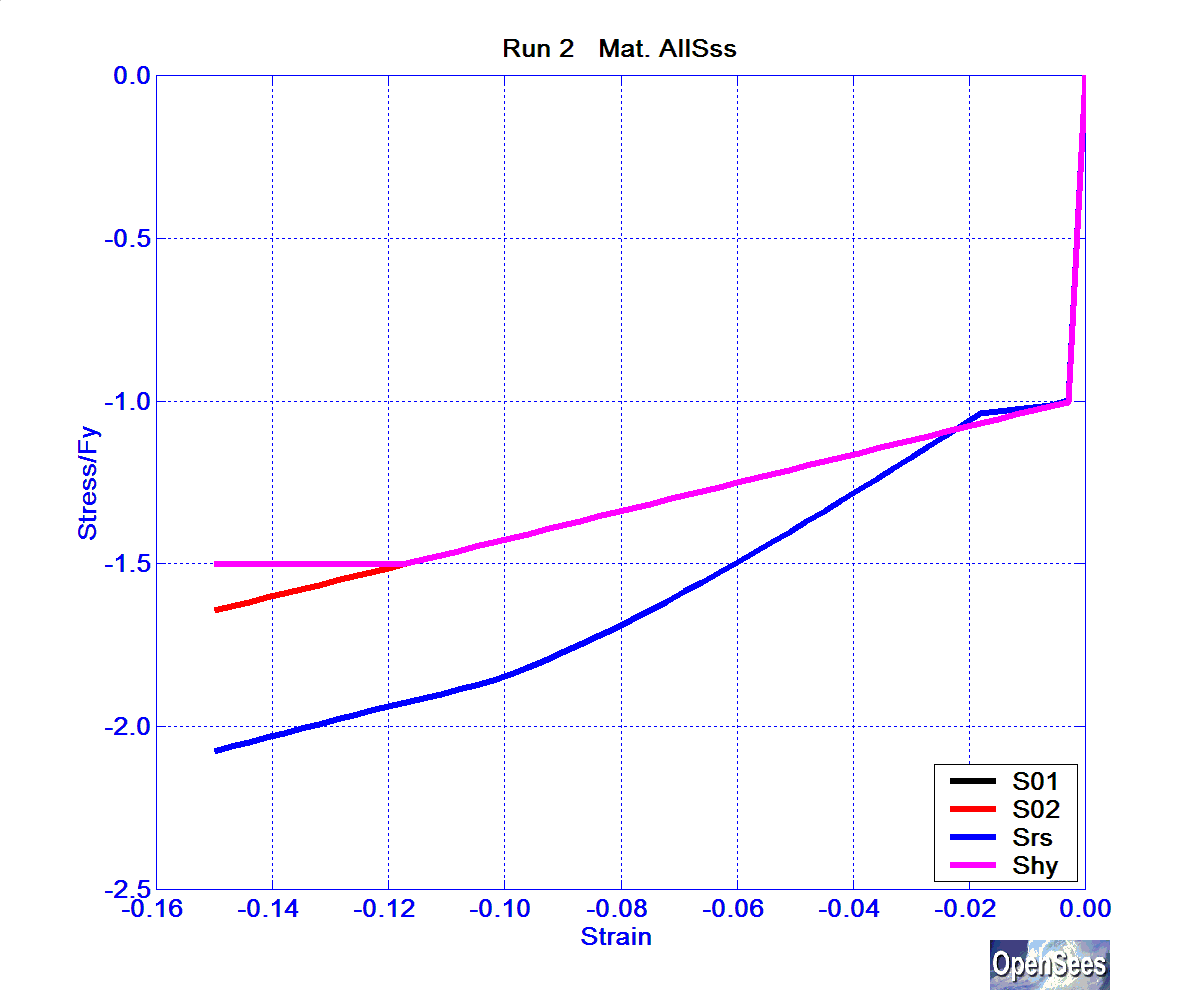
The normalized backbone curve of each of these materials is shown in the following figures, tension in Figure 1, compression in Figure 2.
Figure 1. Backbone Curve for Steel Stress-Strain Relationship -- Tension
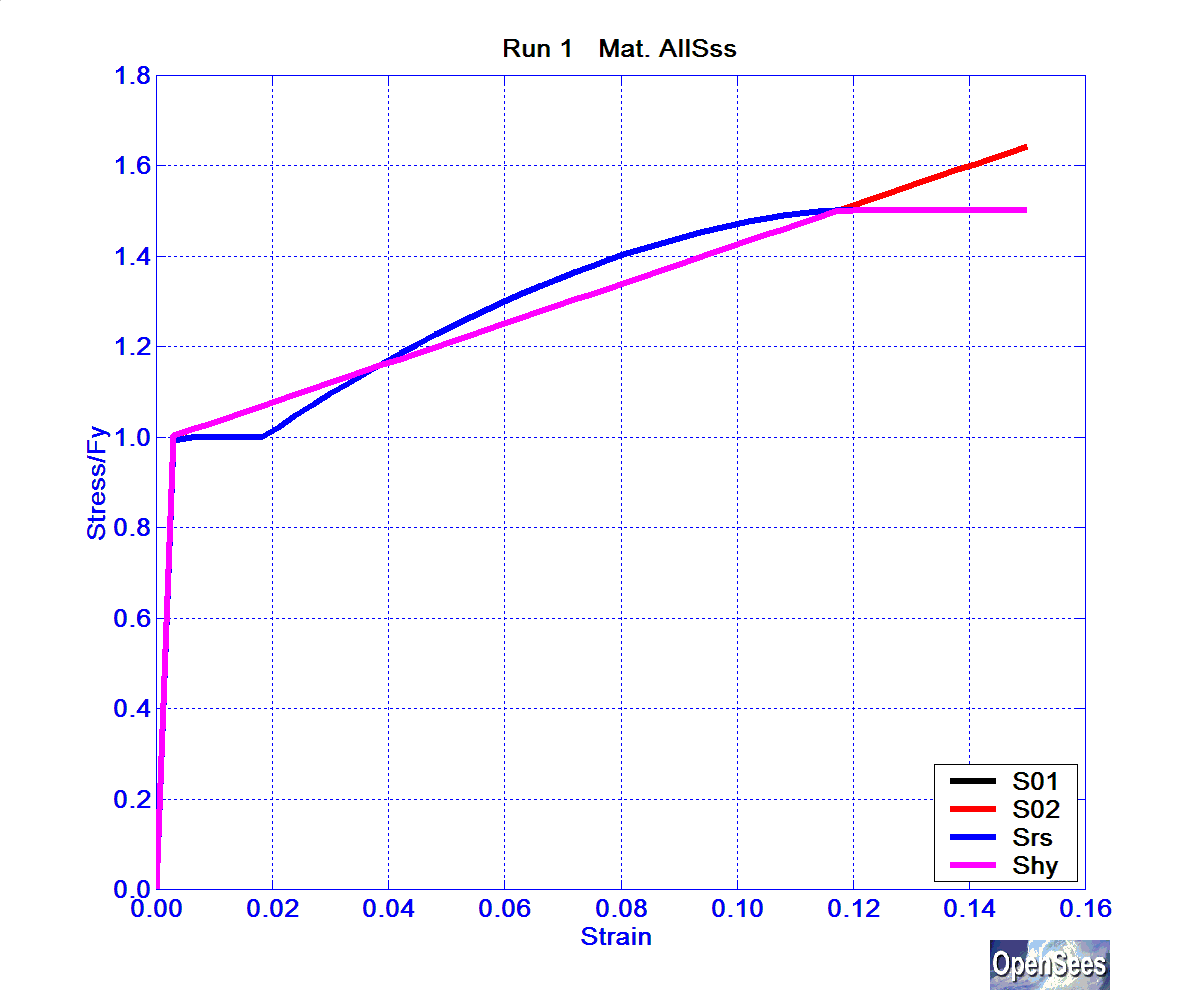
Figure 2. Backbone Curve for Steel Stress-Strain Relationship -- Compression
S10 |
Steel01 |
S20 |
Steel02 |
S30 |
Steel03 |
Srs |
ReinforcingSteel |
Shy |
Hysteretic |