|
|
|
- define model, define & apply gravity
|
|
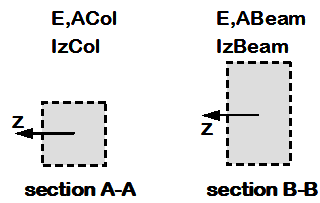
Elastic Section
- Elastic axial and flexural stiffnesses are defined at the section level, using a nonlinear beam-column element
- Build model – nodes, supports, elements, etc.
- elasticBeamColumn elements
- define & apply gravity load
|
|
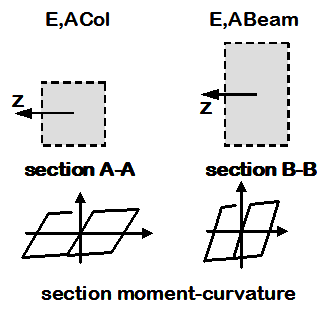
Distributed Plasticity Element, Uniaxial Section
- Elastic axial and inelastic flexural moment-curvature properties are defined at the section level, using a nonlinear beam-column element
- Build model – nodes, supports, elements, etc.
- uniaxial inelastic section (moment-curvature)
- nonlinear beam-column elements
- define & apply gravity load
|
|
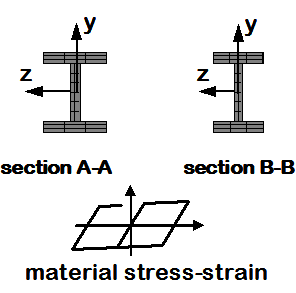
Distributed PlasticityElement, Fiber W-Section
- The section is broken down into fibers where uniaxial materials are defined independently. The program calculates flexural and axial stiffnesses/strength by integrating strains across the section.
- Build model – nodes, supports, elements, etc.
- uniaxial inelastic material (stress-strain)
- Steel fiber W-section
- nonlinear beam-column elements
- define & apply gravity load
|
|
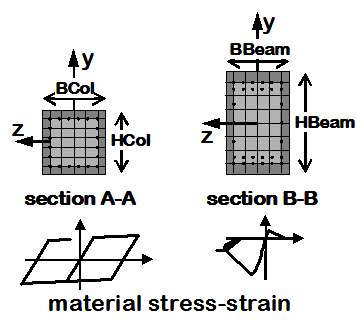
Distributed PlasticityElement, Fiber RC-Section
- The section is broken down into fibers where uniaxial materials are defined independently. The program calculates flexural and axial stiffnesses/strength by integrating strains across the section.
- Build model – nodes, supports, elements, etc.
- uniaxial inelastic material (stress-strain)
- Reinfoced-Concrete fiber section
- nonlinear beam-column elements
- define & apply gravity load
|
|