The following parameter are used in the Hysteretic Material:
$pinchX |
pinching factor for strain (or deformation) during reloading |
$pinchY |
pinching factor for stress (or force) during reloading |
$damage1 |
damage due to ductility: D1(mu-1) |
$damage2 |
damage due to energy: D2(Eii/Eult) |
$beta |
power used to determine the degraded unloading stiffness based on ductility, mu-beta (optional, default=0.0) |
In this study, the parameters are varied independently and compared to the following default parameters:
$pinchX: 1;
$pinchY: 1;
$damage1: 0.0
$damage2: 0.0
$betaMUsteel: 0.0
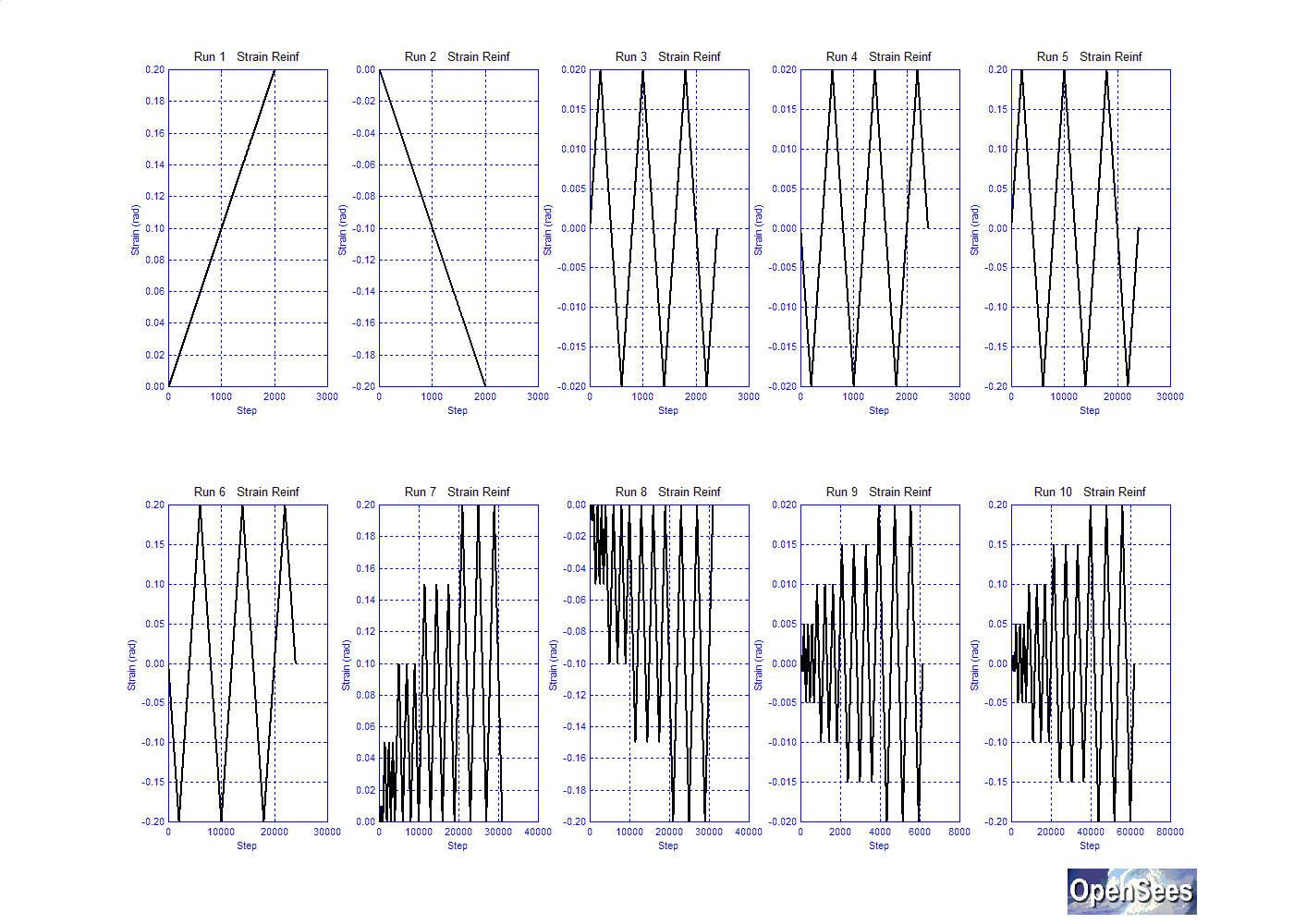
The material was subjected to 10 static strain cycles to demonstrate different behaviors with different cycle pattern and amplitude. The loading cycles are shown in the following figure:
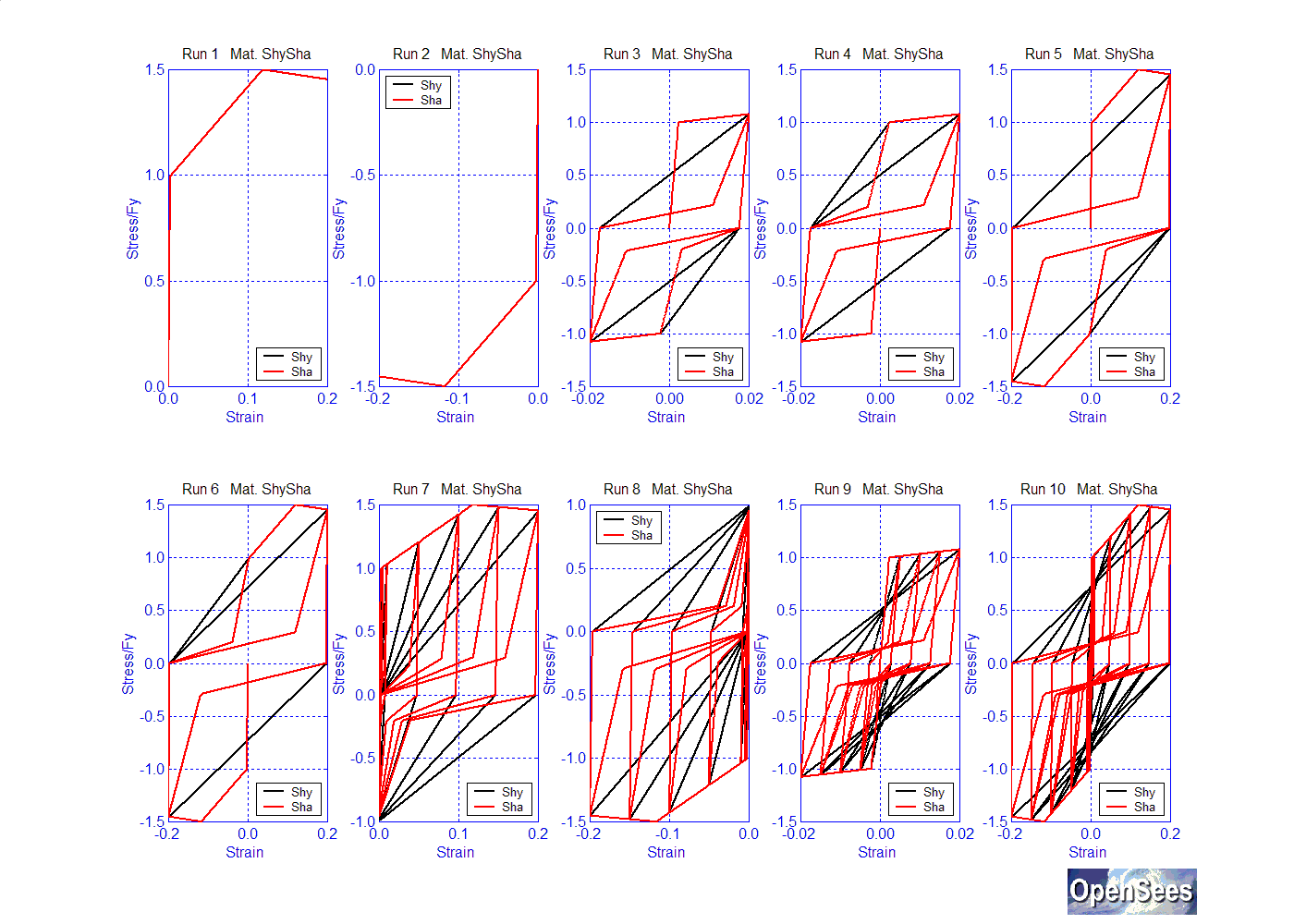
The parameters $PinchX and $PinchY are typically set together, as one represents the modified slope in the X direction, the other in the Y. The following figure shows a comparison of the Hysteretic material using the default values given above (Shy) and the Hysteretic material with the following values (Sha):
$pinchX: 0.8
$pinchY: 0.2;
$damage1: 0.0
$damage2: 0.0
$betaMUsteel: 0.0
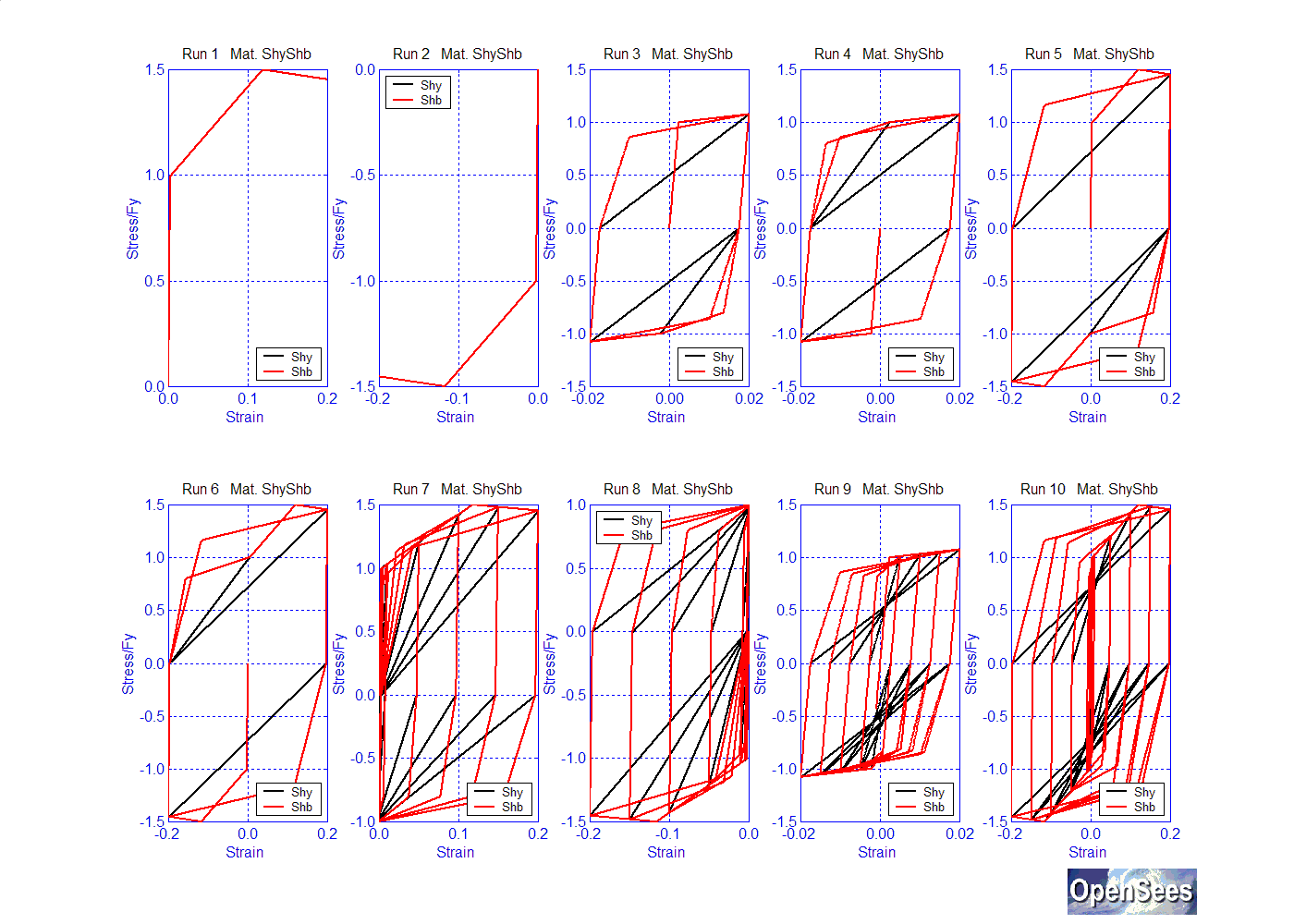
The opposite effect is obtained by switching the values of $PinchX and PinchY (Shb):
$pinchX: 0.2
$pinchY: 0.8;
$damage1: 0.0
$damage2: 0.0
$betaMUsteel: 0.0
The two strength-reducing damage parameters, $damage1 and $damage2, are ductility and energy dependent, respectively. This means that the strength reduction cause by $damage1 is proportional to the strain level -- the larger the strain, the larger the strength reduction. The following figure shows the effects of changing the value of $damage1 (Shc) in comparison to the Hysteretic material with the default values given above:
$pinchX: 1
$pinchY: 1
$damage1: 0.02
$damage2: 0.0
$betaMUsteel: 0.0
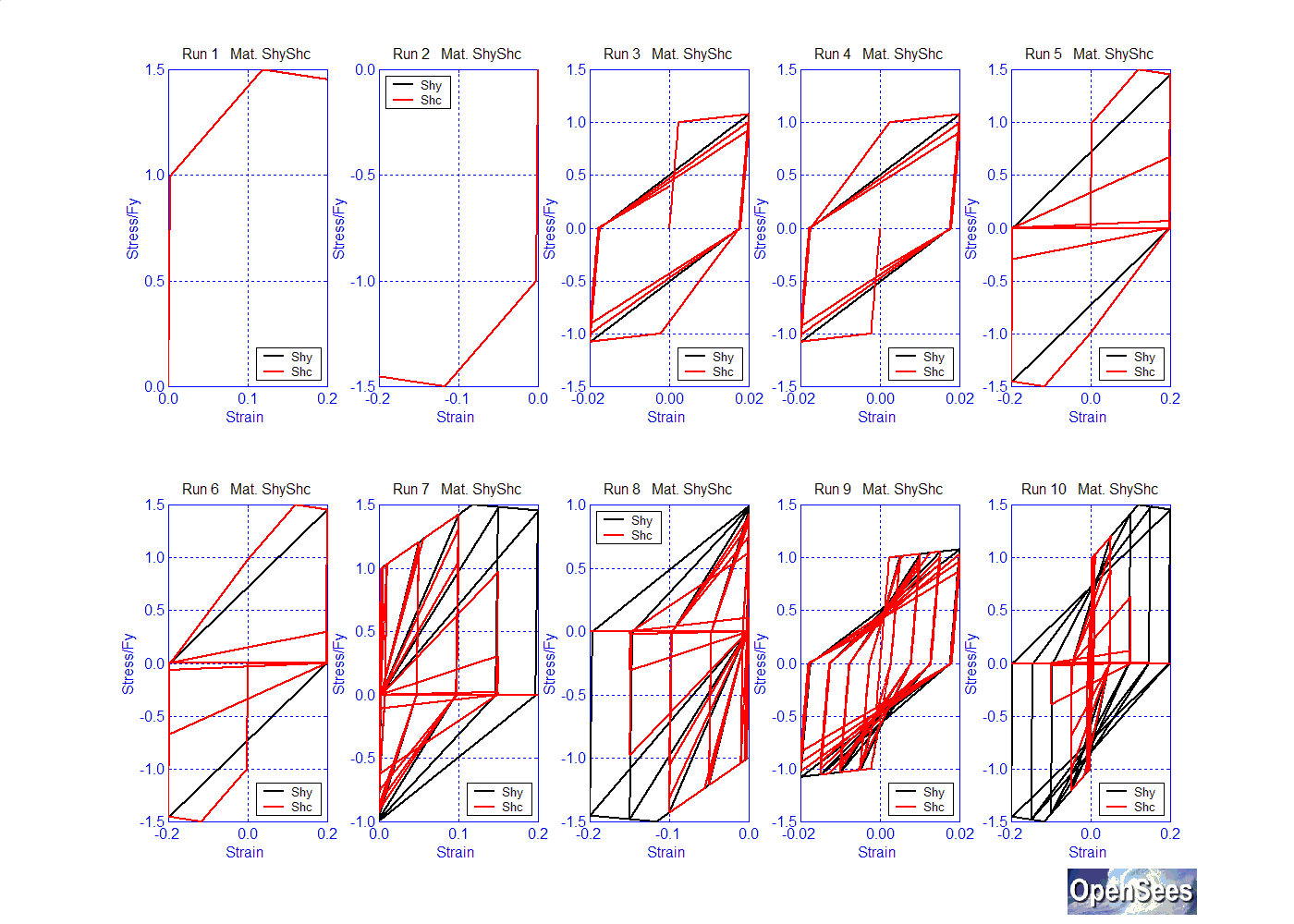
The strength reduction caused by $damage2, on the other hand, is proportional to the energy dissipated by the inelastic strain -- the strength reduction increases with the number of cycles at a fixed strain.
The following figure shows the effects of changing the value of $damage1 (Shd) in comparison to the Hysteretic material with the default values given above:
$pinchX: 1
$pinchY: 1
$damage1: 0.0
$damage2: 0.2
$betaMUsteel: 0.0
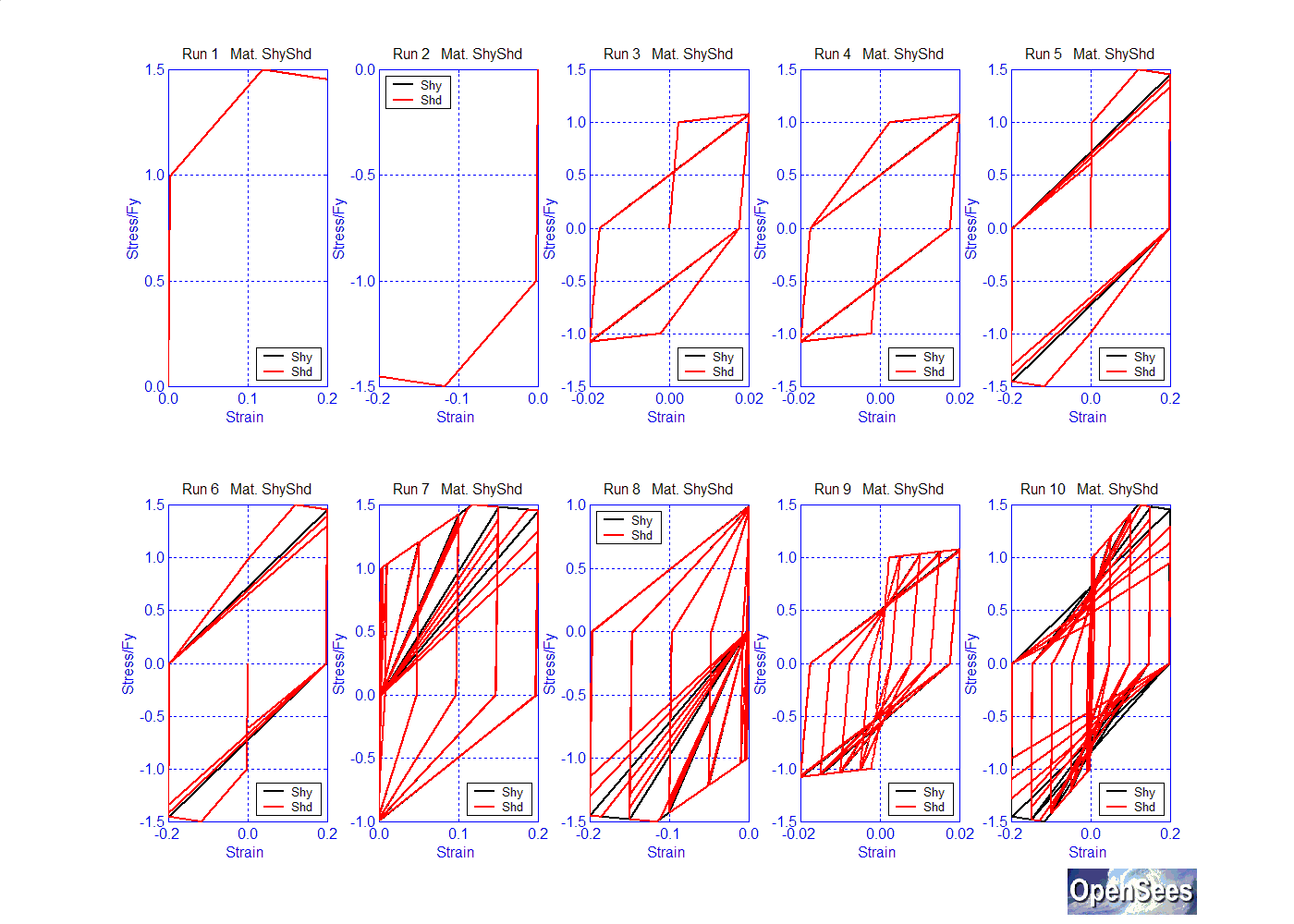
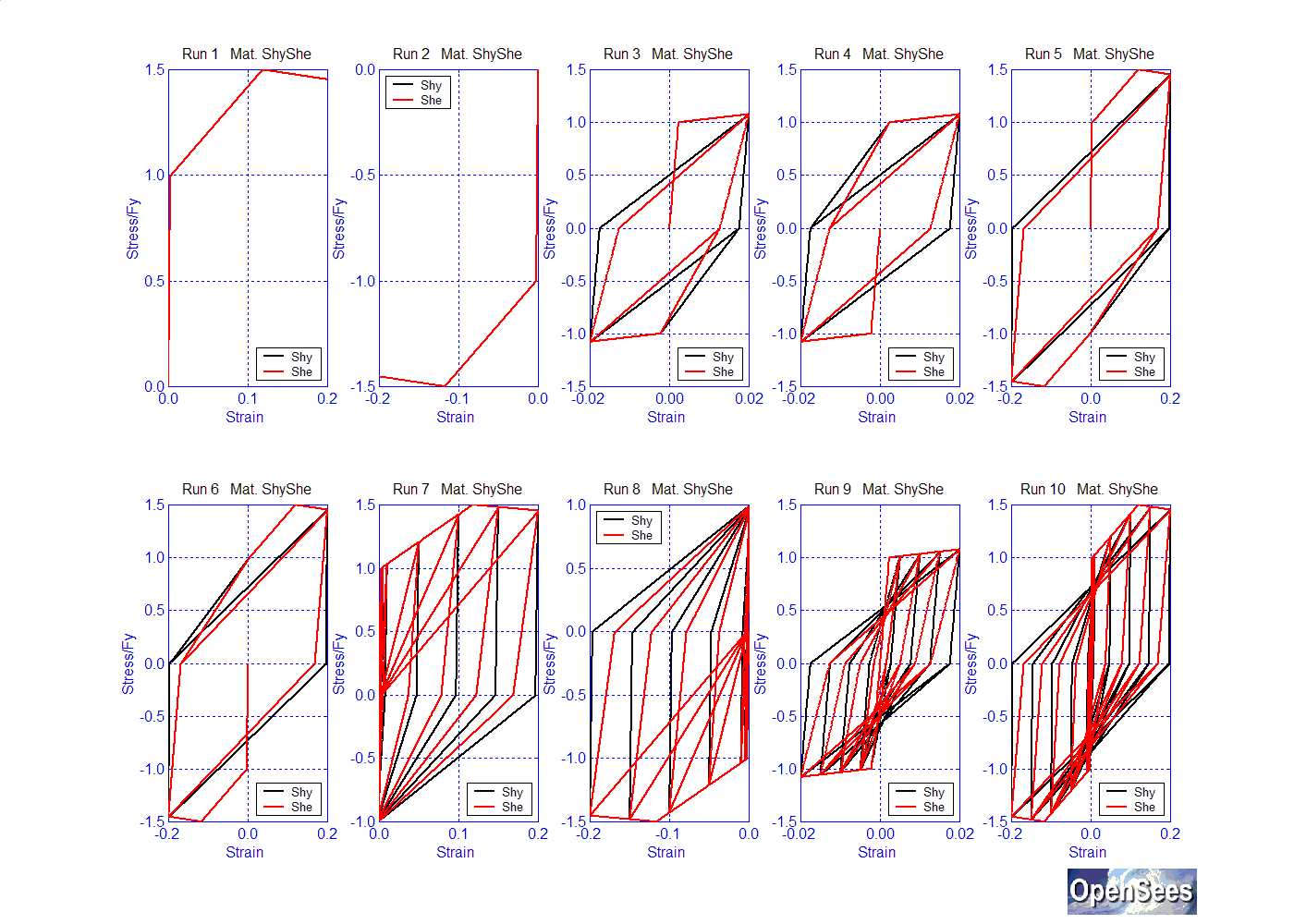
While the default unloading-stiffness parameter is set to 0, a value of 0.5 is shown in the following figure (She):
$pinchX: 1
$pinchY: 1
$damage1: 0.0
$damage2: 0.0
$betaMUsteel: 0.5